Our Services
Our Contact Information
- Nisbetiye, Fecri Ebcioğlu Sk. No: 3E, Beşiktaş/İstanbul
- +90 544 152 34 34
- infodental@eb.clinic
- Monday / Saturday: 9:30 / 19:00
Gum Diseases
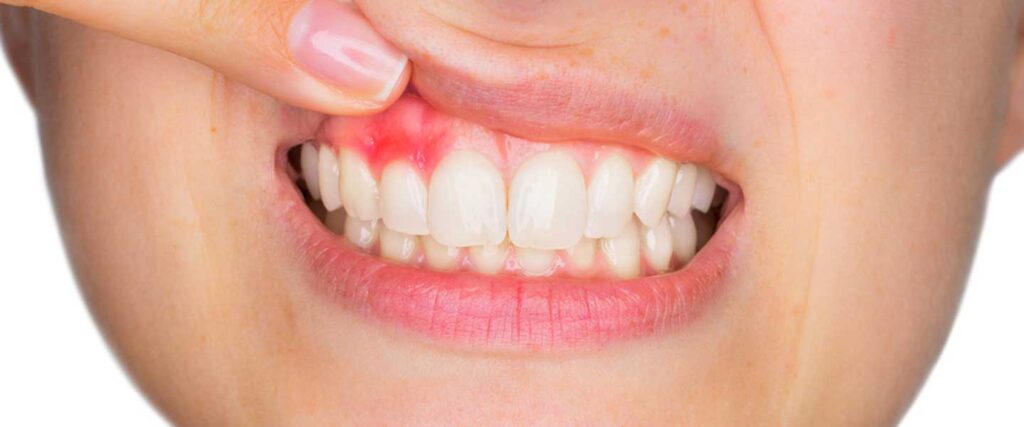
Gum Diseases
Periodontal diseases are various infections of the supporting tissues around the teeth that affect approximately half of adults over the age of 30. As a result of periodontal treatments, the aim is to restore the supporting tissues and keep the teeth healthy in the mouth. These are treatments with high success rates with early diagnosis and correct interventions. First, diseases around the teeth are detected and treatment plans are created accordingly.
Gingivitis (Inflammation of the Gum)
Gingivitis is a condition in which the gums become red, swollen or bleed. This condition, which mostly occurs as a result of inadequate oral hygiene and bacteria in the mouth, aims to prevent the transition to periodontitis, which is a more advanced outcome, through early diagnosis and necessary interventions. Gingivitis often causes problems with eating, brushing teeth and speaking, which negatively affects social life.
Gum Disease Treatment: Restoring Healthy Gums
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gingiva (gums). It is usually caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria on the teeth and gums. Fortunately, gingivitis is typically reversible with appropriate treatment and good oral hygiene practices.
What is Gum Disease?
Gingivitis is a common, mild form of gum disease that can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums, especially when brushing or flossing. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Inflammation
- Plaque Buildup: The primary cause of gingivitis is plaque buildup on the teeth and gums.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing causes plaque to harden into tartar, which can irritate gum tissue.
- Smoking or Chewing Tobacco: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gingivitis.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can affect gum health and contribute to gingivitis.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation or menopause can affect gum health.
Gum Inflammation Treatment
- Professional Dental Cleaning
- Scaling and root planning: Your dentist or dental hygienist will perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and gums. Scaling involves scraping away plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces, while root planning smoothes the root surfaces to help reattach the gums.
- Polishing: Teeth are polished to remove any remaining plaque and stains, making it easier to maintain oral hygiene.
- Improved Oral Hygiene Practices
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums.
- Floss: Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between teeth and under the gum line where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Use an antimicrobial or antibacterial mouthwash to help reduce plaque and kill bacteria.
- Lifestyle and Diet Changes
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke or use tobacco products, quitting can significantly improve gum health and help prevent gingivitis.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support overall oral health. Foods high in vitamin C may be especially beneficial for gum health.
- Regular Dental Checkups
- Routine Visits: Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings every six to twelve months. Regular visits allow your dentist to monitor your gum health, detect signs of gingivitis early, and provide professional cleanings when needed.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions
- Medical Conditions: If you have medical conditions or take medications that contribute to gingivitis, discuss them with your dentist. Managing underlying conditions and adjusting medications may be necessary to improve gum health.
Prevention of Relapse
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene:
- Consistent brushing, flossing, and mouthwash use are essential to prevent gingivitis from recurring.
Regular Dental Care:
- Regular professional cleanings and checkups can help you catch signs of gingivitis early and ensure that your oral hygiene routine is effective.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- To support gum health, avoid tobacco use and follow a nutritious diet.
How Is Gum Disease Diagnosed?
Healthy gums are usually coral pink, firm, and have an orange-peel appearance. When gums become inflamed, this appearance changes and they become darker, looser, and more prone to bleeding. Gingivitis is usually diagnosed by bleeding while eating or brushing, bad breath, and rounding of the gum margins.
What are the causes of gingivitis?
The main cause of gingivitis is inadequate oral hygiene. In addition to poor oral hygiene, the causes of gingivitis include dental trauma: using a hard and incorrect toothbrush, dental floss compressing the gums, local irritants: existing tooth decay, the presence of fillings or prostheses that are incompatible with the gums, various hormonal problems, the use of certain medications or the presence of certain systemic diseases.
How is Gum Inflammation Treated?
Both mechanical and chemical agents are used in the treatment of gingivitis. After the tartar or plaque is cleaned and removed, the treatment is supported with mouthwashes and special gum brushes and check-ups are continued.
What Should Be Considered After Gum Inflammation Treatment?
There may be sensitivity in the gums for a few days after treatment, so it is recommended to stay away from spicy foods and pay attention to hot and cold sensitivity. A situation that negatively affects daily life is usually not observed.
What are Prepless Veneers?
Porcelain veneers are known as prepless laminates or uncut laminates. They can be applied to healthy tooth tissues without making any changes to the tooth surfaces. These applications cover only the front surface of the teeth and are preferred due to their very natural and aesthetic appearance. They are aesthetic applications that provide very good results in closing gaps in the teeth, correcting color and shape disorders of the teeth and completing the smile design. Porcelain veneers are prepared specifically for the person and can be applied to the tooth surfaces using compatible materials without damaging the teeth.
Are Uncut Veneers and Laminate Veneers Different?
Both applications allow the application of aesthetic laminates to the front surface of the teeth, while prepless veneers do not require any abrasion on the teeth before application. Porcelain veneers are applied directly to the tooth surface and can be removed and restored to its former appearance if desired. Laminate veneers, on the other hand, require preparation before application, so they are applied after a small amount of abrasion is made on the tooth surface and if removed, a new restoration is required. Since the procedure time and sessions are shorter in prepless veneers, smile design can be done in a shorter time.
How to Make Uncut Laminate Applications?
During the clinical examination, the teeth that require application are identified. The oral health and harmony of the surrounding tissues are examined, and digital measurements are made with three-dimensional scanners. Photographs and X-rays are also taken, and all personal parameters such as the person’s age, gender, face shape, skin color are checked, and the most ideal smile design is determined in the computer environment. The simulation of the final appearance is examined with the dentists before the application, and the measurements are transferred to the laboratory in the digital environment. In the next session, the veneers are first tried on and then applied to the front surface of the teeth with biocompatible adhesives that do not harm the teeth.
What Should You Know After Applying Uncut Laminates?
Thanks to its ease of application and compatible structures, the patient can return to social life immediately after the procedure. No sensitivity or pain is observed. There is no need to make any changes to the usual brush and floss application in oral care. Since the tissue transitions of prepless veneers are quite natural and extremely compatible with the surrounding tissues, mouth and teeth cleaning can be done easily. Regular attendance to control appointments and regular maintenance of the restorations increase the lifespan of these prostheses.



