Our Services
Our Contact Information
- Nisbetiye, Fecri Ebcioğlu Sk. No: 3E, Beşiktaş/İstanbul
- +90 544 152 34 34
- infodental@eb.clinic
- Monday / Saturday: 9:30 / 19:00
Periodontitis
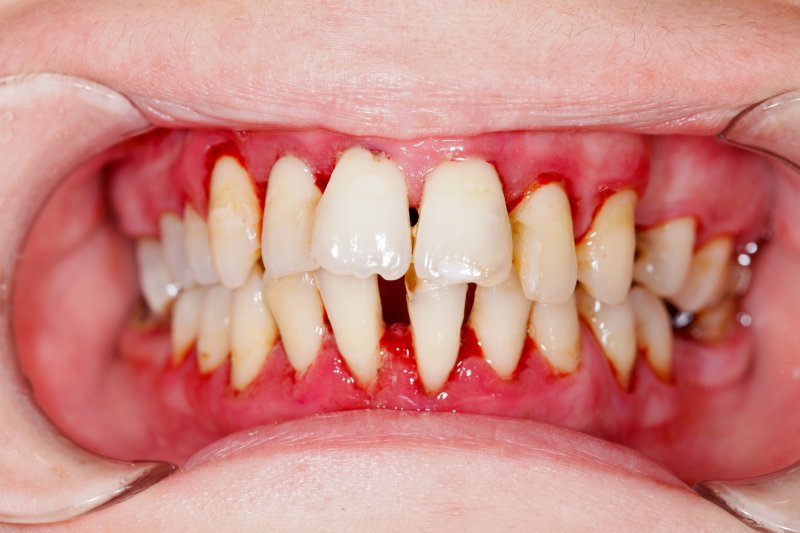
Periodontitis
With the increase of gum inflammation, tissue loss in the jaw bones, loosening of the teeth and even tooth loss are diagnosed as periodontitis. It is an advanced and worsened picture of gingivitis. The reason for this picture is the destruction of these tissues by bacteria in the tissues around the teeth. Periodontitis; It is caused by the change in the bacterial flora in the mouth and the main reason is again inadequate oral hygiene.
Periodontitis Treatment
Periodontitis is an advanced form of untreated gingivitis. It occurs with inflammation of the gums and surrounding tissues and can result in loss of jaw bone, loosening and loss of teeth.
The treatment may include deep cleaning (tartar cleaning and root planing), antibacterial treatments, regulation of oral hygiene, and in advanced cases, surgical procedures (flap operations, graft applications).
Keeping this situation under control is of great importance for both dental health and general health.
What is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis occurs when gum inflammation progresses, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth and form pockets that become infected. This can lead to the loss of tissue and bone that support the teeth. Common symptoms include swollen, bleeding gums, bad breath and tooth mobility.
Why is Rapid Treatment Important?
Addressing periodontitis as soon as possible helps prevent the condition from getting worse. Untreated periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and is linked to other health problems, such as heart disease and diabetes.
Periodontitis Treatment
- Professional Dental Cleaning
- Scaling and root planing: This is the cornerstone of periodontitis treatment. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line, while root planing smoothes the roots of your teeth to help reattach the gums. This deep cleaning helps reduce inflammation and infection.
- Regular Cleanings: You may need more frequent professional cleanings to keep the condition under control and monitor your gum health.
- Improved Oral Hygiene
- Brushing: Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, paying extra attention to the areas where your gums meet your teeth. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid further irritation.
- Floss: Floss daily to clean between your teeth and below the gumline, where your toothbrush can’t reach. This helps remove plaque and prevent new buildup.
- Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Using a prescription mouthwash can help reduce bacteria and control inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for periodontitis and can make treatment less effective. Quitting smoking can greatly improve your gum health and overall oral hygiene.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health. Foods high in vitamin C are especially beneficial for your gums.
- Advanced Treatments
- Medications: Depending on the severity of your periodontitis, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or other medications to help control infection and reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Options: In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair damaged tissue or reduce gum pockets. Procedures such as flap surgery or bone grafts can help restore gum health and support.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Repair
- Regular Checkups: Regular visits to your dentist are essential to monitor your condition and ensure that your gums remain healthy. Your dentist will provide guidance on maintaining good oral hygiene and managing your periodontitis.
- Personalized Care: Your treatment plan will be tailored to your specific needs, and your dentist will work with you to ensure you have the support and resources needed for effective management.
Battling periodontitis requires determination and a proactive approach to oral care. By following your treatment plan and making the necessary lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage periodontitis and achieve better gum health.
If you have any questions or concerns about periodontitis treatment, please contact us. We are here to support you every step of the way and help you achieve a healthier smile.
How Is Periodontitis Diagnosed?
Periodontitis begins with the progression of gingivitis, which is inflammation of the gums. Symptoms such as prolonged bleeding gums, accompanying bad breath, gum recession, and an elongation of the tooth appearance, and sometimes pain are decisive in the diagnosis of periodontitis. In control X-rays, there is a loss of substance in the bones around the teeth and a red and soft profile in the gums. Depending on the amount of tissue loss, the teeth may be wobbly or displaced.
Why Does Periodontitis Occur?
Basically, gum inflammation and recession begin with the formation of a sticky plaque made up of bacteria called dental plaque due to poor oral hygiene. Dental plaque that continues to accumulate under the gums becomes tartar, or dental stone, and begins to destroy the tissues there. Tartar is harder to remove with brushing or flossing, and these layers are full of bacteria. Over time, this tartar layer, which increases in bacterial density, creates pockets in the jawbones and requires professional help to remove them. The risk of developing periodontitis may also increase due to poor eating habits such as vitamin C deficiency, hormonal changes, stress, conditions that reduce immunity such as leukemia or cancer treatments, systemic diseases such as diabetes, obesity or smoking.
How is Periodontitis Treated?
In the treatment of periodontitis, which is an inflammation of the gums, different treatments can be applied depending on the level of the disease. First of all, it is planned to stop tissue destruction by restoring oral hygiene. Dental plaque and tartar are removed from the tooth surfaces and surrounding tissues without damaging these tissues with special devices such as laser, ultrasonic devices and air flow. Since smoothing the root surfaces with special techniques will limit bacterial growth, it is preferred as a preventive treatment. In advanced periodontitis, the aim is to regain the lost gums or hard tissues around the teeth. The soft tissue formed by surgical procedures is arranged and regained. During this procedure, which is applied under anesthesia, the root surfaces and bone tissue are also arranged and cleaned of bacterial structures. If necessary, the hard tissues around the teeth can be regained with the help of bone powder during the surgical procedure. The tissue is closed with very thin special stitches and information is given for the post-surgical procedure. If requested or necessary, all these procedures can be performed under dental sedation or general anesthesia.
Is There a Relationship Between Smoking and Gum Inflammation?
Since nicotine in cigarettes negatively affects blood flow to the tissues and therefore tissue nutrition, smoking can cause gingivitis to be noticed later and tissue destruction to progress more rapidly. In addition, considering the negative effects on tissue healing or the relapse of the disease in the post-treatment period, it can be said that smoking makes it very difficult to maintain gum health.



